Cocoons 101 Video Tutorial
0
Exercise Synopsis
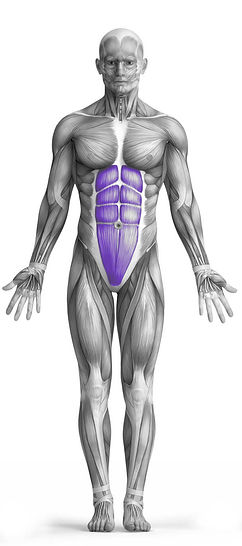
Target Muscle Group
Abs
Secondary Targets
Execution
Compound
Force Type
Core
Required Equipment
Bodyweight
Fitness Level
Intermediate
Variations
None
Alternatives
None
Timer
Hour
Minute
Second
Stopwatch
00:00:00:00
Overview
Cocoons is a dynamic core exercise targeting the abdominal muscles with secondary engagement of the obliques. This bodyweight exercise is performed lying flat on the back with arms extended overhead and legs lifted off the ground. The movement involves contracting the abdominals to lift the upper body while simultaneously bringing the knees towards the chest, resembling the motion of cocooning oneself. This exercise strengthens the core muscles, promotes stability, and enhances overall abdominal strength and endurance without the need for any additional equipment.
How to Perform
Cocoons offer a familiar yet effective approach to abdominal training, with specific attention to safety and efficacy. Follow these step-by-step guidelines for optimal execution:
Begin by lying flat on your back, extending your legs and arms behind your head to ensure proper alignment and engagement of the core muscles.
Initiate the movement by contracting your abdominal muscles, pulling your knees towards your chest while simultaneously lifting your buttocks off the ground. Coordinate this motion with bringing your arms forward and over your knees to execute a controlled crunch.
As you return to the starting position, maintain engagement in your core muscles, ensuring that your legs remain elevated off the ground to preserve the connection between your lower back and the floor, enhancing the effectiveness of the exercise.
Complete the desired number of repetitions with a focus on smooth, controlled movements and maintaining proper form throughout the exercise.
Remember to breathe rhythmically throughout the movement to optimize oxygen flow and muscle engagement.
Incorporating cocoons into your routine can effectively target the abdominal muscles, with additional emphasis on the obliques, utilizing only your body weight as resistance for a convenient yet challenging workout.
★ Bonus: For exercises that involve external weights (such as dumbbells, barbells, or machines), the One Rep Max (1RM) calculator can help you estimate your maximum lifting capacity. Use it to track your strength progress and adjust your training for optimal results.
Tips
Coordinate the movement of your arms and legs simultaneously to evenly activate the core muscles without any discernible bias in muscle engagement.
Concentrate on contracting the core muscles rather than relying on swinging motions of the legs and arms, ensuring maximal effectiveness of the exercise.
Maintain tension on the core muscles by refraining from lowering your heels to the floor, while ensuring that your feet remain elevated sufficiently to maintain contact between the lower back and the ground, minimizing strain on the lumbar region. This precautionary measure is advised to prevent undue stress on the lower back.
How Not to Perform
Avoid relying solely on momentum by swinging your arms and legs to complete the movement. Instead, focus on controlled, deliberate motions to engage the core muscles effectively and prevent unnecessary strain on other muscle groups.
Do not allow your lower back to arch excessively during the exercise, as this can lead to undue stress on the lumbar spine. Maintain proper alignment by keeping your lower back in contact with the ground throughout the movement, ensuring that the emphasis remains on the abdominal muscles.
Refrain from lowering your heels all the way to the ground between repetitions, as this can release tension on the core muscles and diminish the exercise's effectiveness. Instead, keep your feet elevated slightly to maintain constant engagement of the abdominals and obliques.
Avoid holding your breath during the exercise, as this can impede oxygen flow and hinder muscle performance. Remember to breathe rhythmically and naturally throughout the movement to optimize muscle activation and energy expenditure.
Do not rush through the exercise at the expense of proper form and technique. Focus on quality over quantity, performing each repetition with control and intention to maximize the recruitment of the target muscles and minimize the risk of injury.
Avoid overarching your neck or straining your head forward during the exercise. Keep your neck in a neutral position, with your gaze directed towards the ceiling, to maintain proper spinal alignment and reduce the risk of neck strain or discomfort.
Refrain from gripping the floor or pulling on your neck with your hands to assist in lifting your upper body. Instead, rely on the strength of your core muscles to initiate and control the movement, allowing for a more targeted and effective workout for the abs and obliques.
Variations
Variations of fitness exercises refer to different ways of performing a specific exercise or movement to target various muscle groups, intensities, or goals. These variations aim to challenge the body differently, prevent plateaus, and cater to individuals with varying fitness levels.
Alternatives
Alternative exercises in fitness refer to different movements or activities that target similar muscle groups or serve the same training purpose as the primary exercise. These alternative exercises can be used as substitutes when the original exercise is unavailable or challenging to perform due to various reasons such as equipment limitations, injuries, or personal preferences.



