Lever Seated Row 101 Video Tutorial
0
Exercise Synopsis
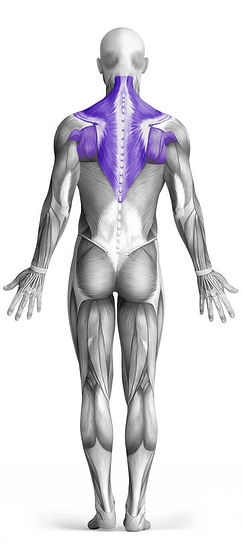
Target Muscle Group
Upper Back
Secondary Targets
Execution
Compound
Force Type
Pull (Bilateral)
Required Equipment
Leverage Machine
Fitness Level
Intermediate
Variations
None
Alternatives
Timer
Hour
Minute
Second
Stopwatch
00:00:00:00
Overview
The Lever Seated Row is a compound pulling exercise that primarily targets the upper back, with secondary engagement of the lats. Performed using a leverage machine, this exercise allows for controlled movement and consistent resistance, making it an effective option for building upper back strength and improving posture. The seated position and chest support help minimize lower back strain while ensuring proper form. By pulling the handles toward the torso while keeping the elbows close to the body, users can maximize muscle activation in the upper back and lats. This exercise is ideal for both beginners and advanced lifters looking to develop back strength and improve pulling power.
How to Perform
Grip the Handles – Sit on the machine with your chest supported and firmly grasp the handles, keeping your arms fully extended.
Initiate the Pull – Engage your upper back muscles and begin pulling the handles toward your torso, keeping your elbows close to your body.
Retract Your Shoulder Blades – As you pull, squeeze your shoulder blades together and continue the movement until your elbows pass behind your back.
Hold Briefly – Pause for a moment at the peak of the contraction to maximize muscle engagement.
Controlled Return – Slowly extend your arms back to the starting position, allowing your shoulders to stretch forward while maintaining control.
Repeat the Motion – Continue for the desired number of repetitions, ensuring smooth and controlled movement throughout.
★ Bonus: For exercises that involve external weights (such as dumbbells, barbells, or machines), the One Rep Max (1RM) calculator can help you estimate your maximum lifting capacity. Use it to track your strength progress and adjust your training for optimal results.
Tips
Maintain Proper Posture – Keep your chest against the pad, back straight, and core engaged throughout the movement.
Grip Firmly – Hold the handles with a neutral or overhand grip, depending on the machine’s design.
Controlled Pulling Motion – Pull the handles toward your torso while keeping your elbows close to your body.
Squeeze Shoulder Blades – Retract your shoulder blades at the end of the pull to fully engage the upper back muscles.
Avoid Using Momentum – Perform the movement in a slow, controlled manner without jerking or relying on momentum.
Full Range of Motion – Extend your arms fully at the start and pull back until your elbows go slightly behind your torso.
Keep Shoulders Down – Prevent your shoulders from shrugging up to avoid unnecessary strain on the traps.
Breathe Properly – Inhale as you extend your arms forward and exhale as you pull the handles back.
Adjust the Machine – Ensure the seat height and chest pad position allow for a comfortable and effective range of motion.
Progress Gradually – Increase resistance over time while maintaining proper form to maximize strength gains and prevent injury.
How Not to Perform
Do Not Round Your Back – Keep your spine neutral and avoid hunching forward, as this can reduce muscle activation and increase the risk of injury.
Avoid Shrugging Your Shoulders – Keep your shoulders down and relaxed to prevent excessive trap engagement and ensure the focus remains on the upper back and lats.
Do Not Use Momentum – Avoid jerking or swinging your body to pull the weight, as this reduces effectiveness and increases injury risk. Perform the movement in a slow, controlled manner.
Don’t Overextend Your Arms – While fully extending your arms at the start, avoid locking out your elbows, which can cause unnecessary joint stress.
Do Not Let Your Chest Leave the Pad – Keep your torso pressed against the pad throughout the movement to maintain stability and prevent unnecessary lower back strain.
Avoid Partial Reps – Ensure you complete the full range of motion by pulling the handles all the way toward your torso and fully extending your arms on the return.
Do Not Grip Too Tightly – Holding the handles with an overly tight grip can cause forearm fatigue and shift focus away from the upper back. Use a firm but relaxed grip.
Don’t Rush the Movement – Performing the exercise too quickly reduces time under tension and makes it less effective for muscle growth. Maintain a steady pace.
Avoid Using Excessive Weight – Lifting too much weight can compromise form and shift the focus away from the target muscles. Use a weight that allows you to maintain proper technique.
Do Not Forget to Breathe – Holding your breath can cause unnecessary strain. Inhale as you extend your arms forward and exhale as you pull the handles back.
Variations
Variations of fitness exercises refer to different ways of performing a specific exercise or movement to target various muscle groups, intensities, or goals. These variations aim to challenge the body differently, prevent plateaus, and cater to individuals with varying fitness levels.
Alternatives
Alternative exercises in fitness refer to different movements or activities that target similar muscle groups or serve the same training purpose as the primary exercise. These alternative exercises can be used as substitutes when the original exercise is unavailable or challenging to perform due to various reasons such as equipment limitations, injuries, or personal preferences.








